News
Site Editor
 Site
https://kingspec.usa02.wondercdn.com/uploads/image/6307135a29359.png
NVMe (nonvolatile memory express) is a new storage access and transport protocol for flash and next-generation solid-state drives (SSDs) that delivers the highest throughput and fastest response times yet for all types of enterprise workloads.
Site
https://kingspec.usa02.wondercdn.com/uploads/image/6307135a29359.png
NVMe (nonvolatile memory express) is a new storage access and transport protocol for flash and next-generation solid-state drives (SSDs) that delivers the highest throughput and fastest response times yet for all types of enterprise workloads.
Understanding SSD Technology: NVMe, SATA, M.2
Views: 11398
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2021-09-03
Origin: Site
What is NVMe?
NVMe (nonvolatile memory express) is a new storage access and transport protocol for flash and next-generation solid-state drives (SSDs) that delivers the highest throughput and fastest response times yet for all types of enterprise workloads.
Today, in both consumer apps and business, users expect ever-faster response times, even as the applications themselves become vastly more complex and resource dependent.
To help deliver a high-bandwidth, low-latency user experience, the NVMe protocol accesses flash storage via a PCI Express (PCIe) bus, which supports tens of thousands of parallel command queues and thus is much faster than hard disks and traditional all-flash architectures, which are limited to a single command queue.
The NVMe specification takes advantage of nonvolatile memory in all kinds of computing environments. And it’s future-proof, extendable to work with not-yet-invented persistent memory technologies.
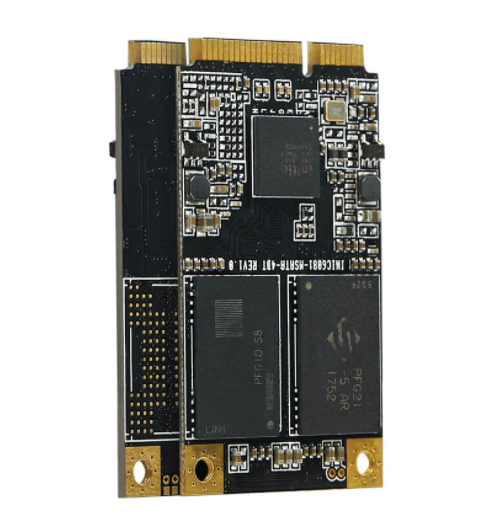
What is SATA?
The SATA (Serial ATA) hard drives is the successor of the traditional PATA (Parallel ATA) Hard drives. It became the central mass storage device on PC. Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, also known as SATA is the new standard for connecting and transferring data components inside of your computer.
What is a SATA hard drive in the flesh is that it’s a bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices. SATA is a serial link – a single cable with at least four wires that form a point-to-point connection between devices.
You can find SATA Hard Drives inside of your desktop computers, laptops, or servers. It is a type of rewritable mass storage devices.
SATA Hard Drives are characterized by good transmission speeds and outstanding storage capacities. They are also supported by virtually all operating systems and computer motherboards.
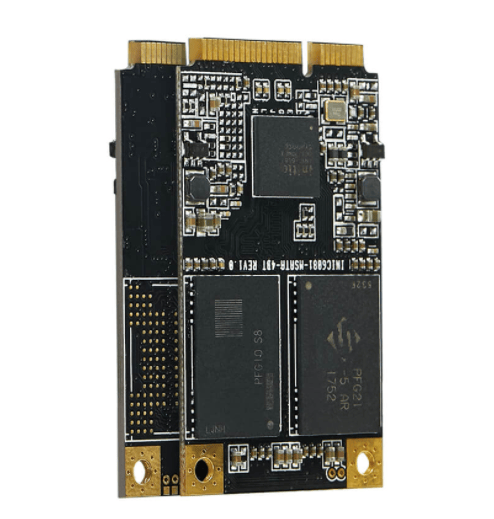
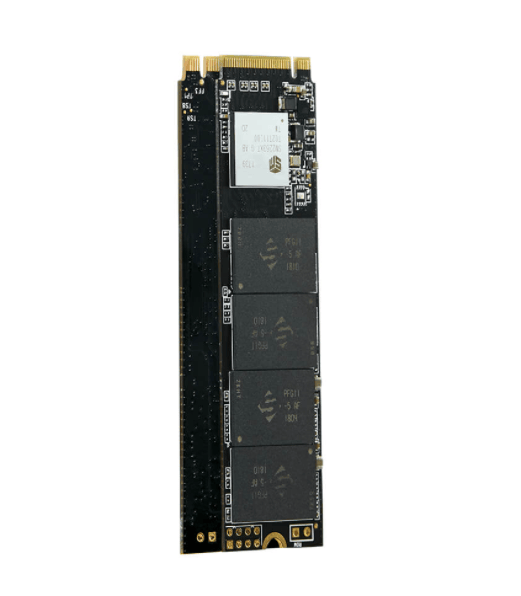
What is M.2?
An M.2 SSD is a small form factor solid-state drive (SSD) that is used in internally mounted storage expansion cards. M.2 SSDs conform to a computer industry specification and are designed to enable high-performance storage in thin, power-constrained devices, such as ultrabook laptops and tablet computers. They are generally smaller than other comparable SSDs, such as the mini Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (mSATA).
SSDs are a form of storage media that saves persistent data on solid-state flash memory. Unlike a hard disk drive (HDD), an SSD has no moving parts to break or spin up or down. The M.2 SSD interface specification was originally known as the Next-Generation Form Factor, but the name was changed to M.2 (pronounced M-dot-2). M.2 SSDs are useful for someone who is building or upgrading a personal computer (PC) or laptop for use cases such as gaming, 3D animation, video editing or large file transfers.
M.2 supports multiple protocols and applications such as Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) and SATA. M.2-compatible products are not limited to solid-state drives either. The specification also supports protocols such as Universal Serial Buses (USBs) and Wi-Fi and can be used in graphics cards and artificial intelligence accelerator cards that use the M.2 specification.
The M.2 form-factor specification was defined by the SATA International Organization, as well as the PCI Special Interest Group -- a consortium of technology industry vendors.
Conclusion
Storage has changed quite a bit over the past few years. Before SSDs, hard drives were the only type of storage that we used, and boy were they slow! We didn’t realize how slow at the time but when SSDs arrived, they were life changing. Few PC upgrades can truly claim that distinction!
As SSDs have evolved into M.2 based PCIe NVMe drives, again we benefit immensely from increased speeds and a much more convenient form factor. While not as life changing as upgrading a hard drive to an SSD, upgrading to an NVMe SSD is still very noticeable and is an upgrade you won’t regret. If you want to know more about SSD, please feel free to contact us!