News
Site Editor
 Site
https://kingspec.usa02.wondercdn.com/uploads/image/6307135a29359.png
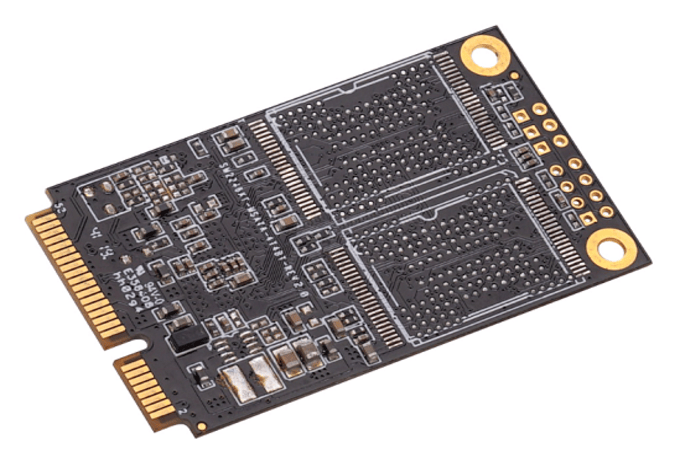
mSATA and mPCIe cards have the same form factor and connector, however they are electrically different micro card formats. If you looked at a mPCIe card and a mSATA card side by side, you'd believe they were the same thing.
An mSATA card can appear to be a mPCIe card, with the same interface and size, and even fit in the same slot—but appearances can be deceiving. mPCIe and mSATA are electrically distinct, while sharing the same physical requirements and even fitting into the same connections.
Site
https://kingspec.usa02.wondercdn.com/uploads/image/6307135a29359.png
mSATA and mPCIe cards have the same form factor and connector, however they are electrically different micro card formats. If you looked at a mPCIe card and a mSATA card side by side, you'd believe they were the same thing.
An mSATA card can appear to be a mPCIe card, with the same interface and size, and even fit in the same slot—but appearances can be deceiving. mPCIe and mSATA are electrically distinct, while sharing the same physical requirements and even fitting into the same connections.
How Does mPCIe Differ From mSATA?
Views: 11544
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2021-11-16
Origin: Site
mSATA and mPCIe cards have the same form factor and connector, however they are electrically different micro card formats. If you looked at a mPCIe card and a mSATA card side by side, you'd believe they were the same thing.
An mSATA card can appear to be a mPCIe card, with the same interface and size, and even fit in the same slot—but appearances can be deceiving. mPCIe and mSATA are electrically distinct, while sharing the same physical requirements and even fitting into the same connections.
Both are small peripheral cards with a similar physical card and socket for enhancing system capability. mPCIe, on the other hand, uses the same PCI Express signals as desktop expansion cards (such as graphics adapters). Whilst mSATA uses the SATA storage interface as SSDs and hard drives.
mSATA also known as mini SATA is the smallest available form of the SATA interface. It is ideal for small form factor applications, including laptops, netbooks, and other mobile devices.
Let's take a look at their full-size equivalents to have a better understanding of these two miniature-card formats.
PCI Express is a serial-connected expansion interface for desktop computers and servers that offers faster speeds and fewer pins than its predecessor (PCI).
PCI Express uses a point-to-point topology rather than the parallel bus architecture of PCI. A lane is a complete duplex pair of differential signals that connects two ends in a serial link.
PCI Express is highly performance-scalable thanks to this design, with up to 32 lanes and rates of up to 1064 MB/s feasibility.
SATA
SATA is a bus interface that uses a serial link to connect host systems to storage devices. SATA is a serial update to PATA that offers faster transfer rates, smaller profile connectors and cables for enhanced system airflow, and a more comprehensive feature set.
Native command queuing is supported by SATA host controllers via AHCI and RAID, as well as classic IDE mode. Similarly, SATA and PCIe employ serial communication with differential signaling to reach speeds of up to 6Gbps with SATA III and has fewer pins than traditional PATA.
PCI-Express Mini
Mini PCI-Express, often known as mPCIe, is a compact peripheral card interface based on PCI Express that is meant for space-constrained devices such as laptops or embedded systems.
mPCIe is a replacement for the older Mini-PCI format, which was a miniature expansion-card form factor based on the older PCI expansion-card standard.
It is widely used in laptops for Wi-Fi or 3G capability. mPCIe cards are much smaller than their desktop equivalents, measuring 30 x 50.95 mm full-size and 30 x 26.8 mm half-size. Their tiny size allows space-constrained devices like laptops, embedded systems, and industrial PCs to be modularly expanded.
Graphics cards, network adapters, serial ports, and other mPCIe expansion modules are as diverse as their full-size PCI Express counterparts. System designers can simply and affordably deliver a variety of configurations to customers, as well as extend product features or signal-handling capability, by employing mPCIe.
However, mPCIe is a scaled-down version of PCI Express, it does differ from its full-size cousin in a few ways. Standard mPCIe cards only use one lane, despite the fact that desktop PCI Express supports up to 32 lanes.
In addition to PCI Express, it supports USB 2.0 signal capability, 3G/4G connectivity is simple to add through mPCIe thanks to additional pins reserved for SIM card signals.
A second lane of PCI Express communication is reserved, albeit it is less typically used and deemed non-standard.
mSATA
The SATA-IO group announced mSATA in 2009 as a dedicated storage interface based on the SATA storage bus interface for space-constrained computers.
mSATA adopted the existing mPCIe physical form factor and connector instead of creating its own.
Also, mSATA is based on an existing and widely used storage interface, mSATA SSDs took off quickly when they first appeared on the market in 2010. Furthermore, storage providers could produce mSATA SSDs easily and quickly.
mSATA cards, like mPCIe, are available in full-size (30.95 mm) and half-size (30.26.8 mm) form factors.
The common connector also enables shared mPCIe/mSATA slots for embedded systems, saving board space while allowing end users to expand with either card type.
Get Your mSATA Card from Us
mSATA SSDs are easily compatible with a variety of device designs. As such, they are extremely popular with device designers and OEMs. Teaming up with Kingspec to provide mSATA cards for will guarantee you the best deals.
Do reach out to us to get mSATA to increase the performance of your computer system.